Understanding Lipids: Types, Functions, and Health Implications And More
Lipids are a diverse group of organic compounds that play crucial roles in the structure and function of living organisms. These substances, which include fats, waxes, phosphatides, and cerebrosides, are primarily characterized by their solubility in nonpolar organic solvents like chloroform and ether, and their insolubility in water. They are integral components of cell membranes, energy storage systems, and various biological functions. This article delves into the different types of lipids, their functions, health benefits, and applications, providing a comprehensive overview of these essential biomolecules.
Types of Lipids
Phospholipids
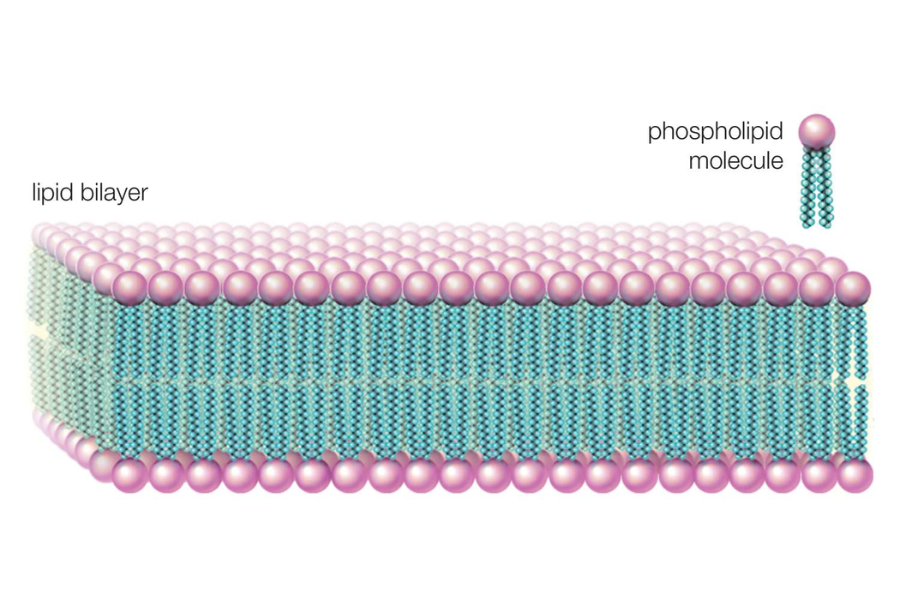
Structure and Function: Phospholipids are fundamental to cell membrane structure. They consist of a glycerol molecule, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group. This unique configuration endows phospholipids with amphipathic properties—having both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) regions. This dual nature allows them to form a bilayer structure in aqueous environments, crucial for creating cell membranes.
Role in Cell Membranes: The phospholipid bilayer is the cornerstone of cell membranes, providing a semipermeable barrier that regulates the entry and exit of substances. This structure maintains cellular integrity and facilitates communication between cells. The fluidity and flexibility of the membrane are essential for various cellular functions, including nutrient transport and signal transduction.
Triglycerides
Energy Storage: Triglycerides, composed of three fatty acids linked to a glycerol backbone, are the body’s primary form of energy storage. They can store more than twice the amount of energy per gram compared to carbohydrates, making them an efficient energy reservoir. Triglycerides are stored in adipose tissue and mobilized when energy is required.
Metabolism and Dietary Sources: Triglycerides are broken down by enzymes called lipases into fatty acids and glycerol. These components are then utilized for energy production. Common dietary sources of triglycerides include oils, butter, and fatty foods. While they are vital for energy, excessive intake can lead to health issues such as obesity and cardiovascular disease.
Steroids
Hormonal Functions: Steroids are a class of lipids that include hormones like testosterone and cholesterol. These molecules are involved in regulating various physiological processes, including metabolism, immune response, and reproduction. Steroids influence many bodily functions through their role as signaling molecules.
Examples (Cholesterol, Testosterone): Cholesterol, a key steroid, is an essential component of cell membranes and a precursor for the synthesis of steroid hormones. Testosterone, another critical steroid, is involved in regulating muscle mass, bone density, and reproductive health.
Waxes
Protective Coatings: Waxes are lipids that function as protective coatings for plants and animals. In plants, they prevent water loss and shield against environmental stresses. In animals, waxes form barriers against external elements, contributing to the maintenance of skin and fur health.
Functions of Lipids
Energy Storage Capabilities: Lipids are the body’s most efficient form of energy storage. One gram of lipids provides more than twice the energy of one gram of carbohydrates. This high energy density is essential for long-term energy storage and survival during periods of food scarcity.
Structural Role in Cell Membranes: Phospholipids and cholesterol are integral to maintaining the structure and fluidity of cell membranes. They help preserve the membrane’s integrity and facilitate the movement of substances in and out of cells. This structural role is critical for various cellular processes, including communication and transport.
Role as Signaling Molecules: Lipid-derived molecules, such as steroid hormones, act as signaling molecules that regulate numerous biological processes. These signaling lipids are crucial for coordinating bodily functions and ensuring proper communication between cells.
Impact on Health (Heart Health, Brain Function): Lipids significantly impact cardiovascular health and brain function. Essential fatty acids, such as omega-3s, are known to reduce inflammation, improve heart health, and support cognitive functions. Maintaining a balanced intake of healthy lipids is vital for overall well-being.
Health Benefits of Lipids
Cardiovascular Health: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, have been shown to reduce LDL cholesterol levels and blood pressure. These healthy fats are beneficial for cardiovascular health and can lower the risk of heart disease and related conditions.
Brain Health: DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid), an omega-3 fatty acid, is a major component of the brain and retina. It plays a critical role in cognitive function and mitigating inflammatory factors, contributing to overall brain health and function.
Essential Fatty Acids: Essential fatty acids, including omega-3 and omega-6, are crucial for maintaining health but cannot be synthesized by the body. A balanced intake of these fatty acids is necessary for reducing inflammation and supporting various physiological functions.
Nutritional Sources of Lipids: Healthy sources of lipids include fatty fish, nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil. Incorporating these foods into your diet ensures a supply of essential nutrients that support overall health. Olive oil, rich in monounsaturated fats, is beneficial for heart health and can be used in cooking and as a salad dressing. Nuts and seeds, such as walnuts and flaxseeds, offer a convenient and nutrient-dense way to increase omega-3 fatty acid intake.
Lipids in Skincare
Lipids play a vital role in skincare by maintaining skin hydration and providing a protective barrier. They prevent moisture loss and help keep the skin supple and smooth. Certain lipids also possess anti-inflammatory properties, making them beneficial for soothing irritated skin and reducing redness. By forming a barrier against environmental damage, lipids help maintain skin integrity and appearance. They also support skin elasticity and reduce the appearance of wrinkles, contributing to a youthful and radiant complexion.
Environmental Impact of Lipids
Natural lipids are biodegradable, making them environmentally friendly compared to synthetic chemicals. Their ability to break down naturally reduces their environmental impact. Lipids are essential for the energy budgets of organisms and play critical roles in various biological cycles. They provide energy for many animals and contribute to the health and balance of ecosystems. Unlike synthetic chemicals, natural lipids are less likely to accumulate in ecosystems, making them preferable for use in pharmaceuticals and other applications.
Lipids in Pharmaceuticals
Liposomal drug delivery systems utilize lipids to encapsulate drugs, enhancing their stability and bioavailability. This method ensures that medications are more effective and targeted in their action. Lipid-based delivery systems are particularly useful for fat-soluble vitamins and other compounds, improving their absorption and effectiveness.
Common Misconceptions About Lipids
A common misconception is that all fats lead to weight gain. However, healthy fats, such as those found in nuts and olive oil, are essential for maintaining good health and do not necessarily contribute to obesity when consumed in moderation. Not all fats are harmful; monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are beneficial for health and should be included in a balanced diet. Eliminating all fats can lead to nutrient deficiencies and negatively impact health.
Future Prospects and Research
Ongoing research in lipid science continues to uncover new benefits and applications for lipids. Advances in understanding lipid metabolism and functions hold promise for innovative health solutions and therapies. Future research may reveal novel uses for lipids in areas such as superior drug delivery systems, enhanced dietary supplements, and new skincare products. The potential for lipids to improve health and industry applications is vast and exciting.
Lipids are essential biomolecules with diverse roles and applications. From their structural importance in cell membranes to their impact on health and the environment, understanding lipids is crucial for appreciating their significance in both biology and daily life. As research progresses, the potential for new lipid-based innovations continues to expand, promising advancements in health, medicine, and beyond.
Explore the latest news and updates on trending topics at Newstribune.blog.